Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (23): 3698-3704.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1316
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment and identification of a mouse model of vascular endothelial cell knockout DEPTOR gene
Ding Yan, Meng Biying, Xiang Guangda
- (General Hospital of Middle Theater Command of Chinese PLA of Southern Medical University, Wuhan 430700, Hubei Province, China)
-
Received:2019-01-30Online:2019-08-18Published:2019-08-18 -
Contact:Xiang Guangda, MD, Chief physician, General Hospital of Middle Theater Command of Chinese PLA of Southern Medical University, Wuhan 430700, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Ding Yan, Doctoral candidate, Physician, General Hospital of Middle Theater Command of Chinese PLA of Southern Medical University, Wuhan 430700, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81370896 (to XGD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ding Yan, Meng Biying, Xiang Guangda. Establishment and identification of a mouse model of vascular endothelial cell knockout DEPTOR gene[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3698-3704.
share this article

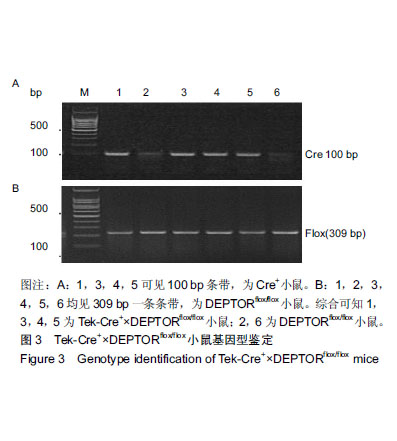
2.3 血管内皮细胞敲除DEPTOR基因纯合子小鼠的鉴定结果 经PCR电泳实验结果统计共鉴定出基因型为Tek- Cre+×DEPTORflox/flox的小鼠25只、单纯的DEPTORflox/flox小鼠40只。见图3。经测量和称质量统计分析,2月龄的敲除鼠Tek-Cre+×DEPTORflox/flox与单纯DEPTORflox/flox的对照小鼠体长分别为(18.61±1.14),(18.65±1.40) cm,t=0.119,P=0.905;体质量分别为(25.84±1.99),(25.06±2.15)g,t=1.431,P=0.158。二者体长、体质量比较,差异无显著性意义(P均> 0.05)。"
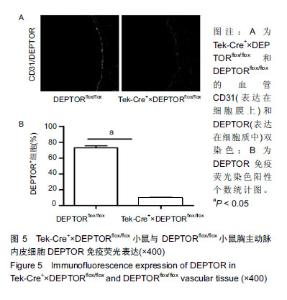
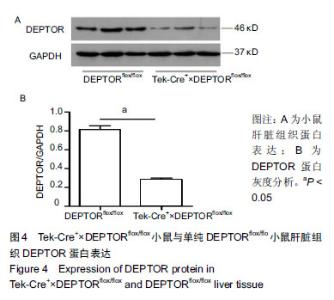
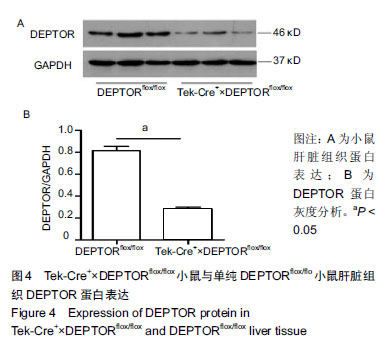
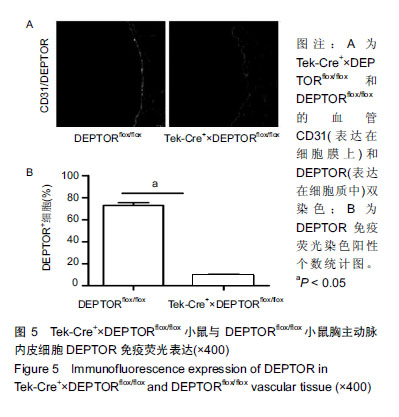
2.5 Tek-Cre+×DEPTORflox/flox小鼠与DEPTORflox/flox小鼠胸主动脉DEPTOR免疫荧光染色结果 Tek-Cre+× DEPTORflox/flox和DEPTORflox/flox小鼠的胸主动脉进行CD31(表达在血管内皮细胞膜上)和DEPTOR(表达在细胞质中)的免疫荧光双染色,CD31是一种血管内皮细胞膜特异性的标志蛋白。染色结果发现在CD31染色的胸主动脉内皮细胞DEPTOR阳性个数表达中,Tek-Cre+×DEPTORflox/flox小鼠血管内皮细胞DEPTOR阳染个数明显低于DEPTORflox/flox小鼠,说明Tek-Cre+×DEPTORflox/flox小鼠成功在血管内皮细胞上敲除了DEPTOR基因,见图5。 "
| [1]Birbrair A, Zhang T, Wang Z M, et al. Type-2 pericytes participate in normal and tumoral angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2014;307(1):C25-C38.[2]Kim B, Lee Y, Yoo H, et al. Anti-angiogenic activity of thienopyridine derivative LCB03-0110 by targeting VEGFR-2 and JAK/STAT3 Signalling. Exp Dermatol. 2015;24(7):503-509.[3]王丽,李录英,陆齐,等. CD73在乳腺癌血管新生中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015,12(10):1843.[4]Li S,Haigh K,Haigh JJ,et al.Endothelial VEGF sculpts cortical cytoarchitecture.J Neurosci.2013;33(37):14809-14815.[5]江克华,董自强,宋兴福,等.PI3K/PTEN信号通路与肿瘤血管形成关系的研究进展[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(22):4169-4170.[6]李景,付焱,肖光雄,等.源于乳腺癌干细胞的内皮细胞参与肿瘤血管形成的实验研究[J].医学研究生学报, 2016,29(11): 1191-1196.[7]陈银涛,于秉治,武迪迪. PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路及临床相关肿瘤抑制剂[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2014,30(10):949-956.[8]廖明娟,陈红风.PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路抑制剂在乳腺癌中的研究进展[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志,2012,19(3):230-234.[9]王法斌,李京波. 他汀类药物对血管形成的作用及分子机制[J]. 实用医学杂志,2012,28(23):4018-4020.[10]许小兵,郭美霞,金鑫鑫,等. 塞来昔布抑制血管内皮细胞迁移的实验研究[J]. 医学研究生学报,2017,30(6):601-605.[11]王宇霆,周海燕,吕小翠.白藜芦醇对过氧化氢氧化应激损伤人脐静脉血管内皮细胞的保护作用[J].中华医学杂志, 2013,93(15): 1174-1177.[12]马丽娜,陈北冬,赵艳阳,等.银杏内酯B对内皮细胞的保护作用及分子机制研究[J].中国药理学通报,2013,29(2):189-193.[13]Ghosh CC, Mukherjee A, David S, et al. Angiopoietin-1 Requires Oxidant Signaling through p47phox to Promote Endothelial Barrier Defense.PLoS One. 2015;10(3): e119577.[14]周政荣,丁丽娜.冠心病合并糖尿病应用奥美沙坦酯对患者血管内皮细胞功能的影响作用[J].北方药学,2018,15(11):29-30.[15]王志钢,吴应积,旭日干. mTOR信号通路与细胞生长调控[J]. 生物物理学报,2007,23(5):333-342.[16]高阳,田树旭,常小丽,等.雷帕霉素靶蛋白的蛋白信号通路及其与代谢性疾病相关性[J].医学研究生学报,2010,23(2):196-201.[17]Chung AS,Lee J, Ferrara N. Targeting the tumour vasculature: insights from physiological angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(7):505-514.[18]Zeng Q,Wu Z,Duan H,et al.Impaired tumor angiogenesis and VEGF-induced pathway in endothelial CD146 knockout mice. Protein Cell.2014;5(6):445-456.[19]Huang B,Wang Y,Wang W,et al. mTORC1 Prevents Preosteoblast Differentiation through the Notch Signaling Pathway. PLOS Genetics.2015;11(8):400-426.[20]Ma A, Wang L, Gao Y, et al. Tsc1 deficiency-mediated mTOR hyperactivation in vascular endothelial cells causes angiogenesis defects and embryonic lethality. Human Molecular Genetics.2014,23(3):693-705.[21]Duan S, Shafi JRS, Kuchay S, et al. mTOR Generates an Auto-Amplification Loop by Triggering the bTrCP- and CK1a-Dependent Degradation of DEPTOR. 2011:44: 317-324.[22]Zhan JK, Wang YJ, Wang Y, et al. Adiponectin attenuates the osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells through the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Exp Cell Res.2014; 323(2):352-358.[23]Laplante M, Horvat S, Festuccia WT, et al. DEPTOR Cell-Autonomously Promotes Adipogenesis, and Its Expression Is Associated with Obesity. Cell Metab. 2012; 16(2):202-212.[24]Kazi AA,Hong-Brown L,Lang SM, et al. Deptor knockdown enhances mTOR Activity and protein synthesis in myocytes and ameliorates disuse muscle atrophy. Mol Med.2011; 17(9-10):925-936.[25]Bruneau S,Nakayama H,Woda CB,et al.DEPTOR regulates vascular endothelial cell activation and proinflammatory and angiogenic responses. Blood. 2013;122(10):1833-1842.[26]Liu M, Wilk SA, Wang A, et al. Resveratrol inhibits mTOR signaling by promoting the interaction between mTOR and DEPTOR.J Biol Chem.2010;285(47):36387-36394.[27]赖舒畅,邱鸿,王肖,等.条件性胰岛β细胞DEPTOR基因敲除小鼠构建及鉴定[J].实用医学杂志,2018,34(4):552-555.[28]王志蕊,刘西梅,周荆荣,等. Cre-LoxP重组系统删除内源性选择标记基因的效能评价[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2014, 30(2):194-201.[29]吴壮,徐军.Cre/Loxp位点重组酶系统在疾病动物模型建立中的应用[J].国外医学(呼吸系统分册),2004,24(4):254-256.[30]任荣荣,王英伟. Cre/Loxp系统的应用及进展[J].广州医学院学报,2008,36(2):78-80.[31]Hong J,Liu R,Chen L,et al. Conditional knockout of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 in vascular endothelial cells accelerates atherosclerotic plaque development in mice. Thromb Res.2016;137:148-156.[32]桑璐,郭英,任立明,等.利用Cre/lox重组系统在转基因动物中筛选高效表达外源基因的"友好"基因座[J]. 高技术通讯,2004, 14(12):43-49.[33]Campochiaro PA, Sophie R, Tolentino M, et al. Treatment of diabetic macular edema with an inhibitor of vascular endothelial-protein tyrosine phosphatase that activates tie2.Ophthalmology.2015;122(3):545-554.[34]Sarkar K, Rey S, Zhang X, et al. Tie2-dependent knockout of HIF-1 impairs burn wound vascularization and homing of bone marrow-derived angiogenic cells. Cardiovascular Res. 2011;93(1):162-169.[35]Kawakami Y, Ii M, Matsumoto T, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis in Tie2-Lineage Cells Including Endothelial Progenitor Cells Contributes to Bone Fracture Healing. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(1):95-105.[36]Catena V,Fanciulli M.Deptor: not only a mTOR inhibitor. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):12.[37]Ji YM, Zhou XF, Zhang J, et al. DEPTOR suppresses the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and predicts poor prognosis.Oncotarget.2016;7(12):14188-14198.[38]Chen L, Liu T, Tu Y, et al. Cul1 promotes melanoma cell proliferation by promoting DEPTOR degradation and enhancing cap-dependent translation. Oncol Rep.2016; 35(2):1049-1056.[39]Caron A,Mouchiroud M,Gautier N,et al.Loss of hepatic DEPTOR alters the metabolic transition to fasting. Molecular Metabolism.2017;6(5):447-458.[40]Dong X,Wang L, Han Z, et al. Different functions of DEPTOR in modulating sensitivity to chemotherapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 2017;353(1):35-45.[41]Zhou X,Guo J,Ji Y,et al. Reciprocal Negative Regulation between EGFR and DEPTOR Plays an Important Role in the Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer Res. 2016; 14(5):448-457.[42]Srinivas KP, Viji R, Dan VM, et al. DEPTOR promotes survival of cervical squamous cell carcinoma cells and its silencing induces apoptosis through downregulating PI3K/AKT and by up-regulating p38 MAP kinase. Oncotarget. 2016;7(17): 24154-24171.[43]Agrawal P,Reynolds J,Chew S,et al.DEPTOR is a stemness factor that regulates pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem.2014;289(46):31818-31826.[44]González-Terán B, López JA, Rodríguez E, et al. p38γ and δ promote heart hypertrophy by targeting the mTOR-inhibitory protein DEPTOR for degradation. Nat Commun. 2016;7: 10477.[45]Ding Y,Shan L,Nai W,et al.DEPTOR Deficiency-Mediated mTORc1 Hyperactivation in Vascular Endothelial Cells Promotes Angiogenesis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(2): 520-531 [46]Xu N,Guan S,Chen Z,et al.The alteration of protein prenylation induces cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through Rheb-mTORC1 signalling and leads to chronic heart failure. J Pathol.2015;235(5):672-685.[47]Nitta N, Nakasu S, Shima A, et al. mTORC1 signaling in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Surg Neurol Int.2016;7(Suppl 17):S475-S480.[48]Lorbeer R,Baumeister SE,Dorr M,et al.Angiopoietin-2, its soluble receptor Tie-2 and subclinical cardiovascular disease in a population-based sample. Heart.2015;101(3):178-184.[49]Kisanuki YY, Hammer RE, Miyazaki J,et al.Tie2-Cre transgenic mice: a new model for endothelial cell-lineage analysis in vivo. Dev Biol.2001;230(2):230-242.[50]Barry DM, Xu K,Meadows SM, et al. Cdc42 is required for cytoskeletal support of endothelial cell adhesion during blood vessel formation in mice. Development.2015;142(17): 3058-3070.[51]Ohashi K,Ouchi N,Higuchi A, et al. LKB1 deficiency in Tie2-Cre-expressing cells impairs ischemia-induced angiogenesis.J Biol Chem.2010;285(29):22291-22298.[52]丁燕,赖丽芬,奈文青,等.血管内皮细胞敲除Rheb基因杂合子小鼠模型建立及意义[J].山东医药,2017,57(36):34-36.[53]李娇,陈永文,张庆镐. CD1d基因敲除小鼠拮抗DSS诱导结肠炎[J].免疫学杂志,2018,34(9):759-764. |
| [1] | Zhou Quan, Zhang Yanan, Bai Yiguang, Zhang Qiong, Nong Haibin, Liu Mingfu, Zeng Gaofeng, Zong Shaohui. Effect of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 regulating osteoclasts on bone mineral density in osteoporotic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4680-4684. |
| [2] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Liu Tao, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin . Relationship between extracellular vesicles and radiation-induced tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2121-2126. |
| [5] | Zhang Jian, Chen Miao, Li Weixin, Ye Yichao, Xu Huiyou, Ma Ke, Chen Xuyi, Sun Hongtao, Zhang Sai. Collagen/heparin sulfate scaffolds loaded with brain-derived neurotrophic factor promote neurological and locomotor function recovery in rats after traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5538-5544. |
| [6] | Chen Jia, Yang Yiqiang, Hu Chen, Chen Qi, Zhao Tian, Yong Min, Ma Dongyang, Ren Liling. Fabrication of prevascularized osteogenic differentiated cell sheet based on human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4934-4940. |
| [7] | Zhan Xiaoshu, Luo Huina, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Shengfeng, Wang Bingyun, Bai Yinshan, Chen Zhisheng, Liu Canying, Ji Huiqin. Effects of exosomes derived from canine umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration and apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(29): 4637-4643. |
| [8] | Yuan Tao1, Wang Yongzhuo1, Huang Yuanzhang1, Xi Gang1, Wei Lei1, 2, Zhang Min1. Establishment of Indian hedgehog protein conditional knockout mouse models based on Cre/LoxP system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3013-3018. |
| [9] | Luo Su-yi, Huang Wei, Wang Jing, Wang Xi-yun, Li Jin-tao. Effects of tropomyosin 4 applied in spinal cord injuries via lentiviral vector recombination and the underlying mechanism: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(37): 5573-5579. |
| [10] | Chen Rui-jun, Huang Xiao-feng, Zhang Fang-ming. Time-specific gene knockout technology: model establishment, present and future [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(18): 2725-2730. |
| [11] | Wei Wei, Li Xiao-ling, Yuan Wen-chang. Construction and application of Staphylococcus aureus gene knockout plasmid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(5): 799-804. |
| [12] | Li Lin-ge, Feng Juan, Hu Bin, Shou Xi, Zhang Chun, Tian Yu, Jiang Chun-rong, Zhang Yu, Zhang Hua . Establishing mouse models of allergic rhinitis by knocking out H2-eb1 gene [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(27): 4417-4422. |
| [13] | Mori Gele, Shao Zeng-wu. Restraining degeneration of intervertebral discs by transplantation of Notch-1knockout rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(36): 6403-6408. |
| [14] | Li Yan, Zhang Jian-she, Dong Xiu-hua . In vitro pre-vascularized tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(33): 6013-6020. |
| [15] | Wang Jing, Dong Fang-fang, Li Xiao-feng, Xu Jin-hai, Shu Bing, Shi Qi, Wang Yong-jun, Zhou Chong-jian. 低氧诱导因子1α基因敲除小鼠椎间盘退变与益气化瘀方的干预 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(24): 4481-4487. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||